Table of Contents
- 1 UNDERSTANDING 5G TECHNOLOGY
- 2 THE INTERNET OF THINGS (IOT) AND ITS EVOLUTION
- 3 THE SYNERGY BETWEEN 5G AND IOT
- 4 5G AND SMART CITY INNOVATIONS
- 5 CHALLENGES AND CONSIDERATIONS
- 6 5. SKILL DEVELOPMENT AND WORKFORCE TRAINING:
- 7 CASE STUDIES OF 5G-ENABLED SMART CITIES
- 8 1. SEOUL, SOUTH KOREA
- 9 2. BARCELONA, SPAIN
- 10 3. SINGAPORE
- 11 4. NEW YORK CITY, USA
- 12 THE FUTURE OF 5G AND SMART CITIES
- 13 1. INTEGRATION OF AI AND MACHINE LEARNING
- 14 2. ADVANCED ROBOTICS AND AUTOMATION
- 15 3. ENHANCED VIRTUAL AND AUGMENTED REALITY
- 16 4. SUSTAINABLE URBAN DEVELOPMENT
- 17 5. PERSONALIZED AND CITIZEN-CENTRIC SERVICES
- 18 6. ENHANCED PUBLIC TRANSPORTATION SYSTEMS
- 19 7. SMART HEALTHCARE SYSTEMS
- 20 8. SMART EDUCATION AND LEARNING ENVIRONMENTS
- 21 9. ENHANCED RETAIL EXPERIENCES
- 22 10. INTELLIGENT BUILDING MANAGEMENT
- 23 11. ENHANCED ENVIRONMENTAL SUSTAINABILITY
- 24 12. ADVANCED PUBLIC SAFETY AND EMERGENCY RESPONSE
- 25 13. ENHANCED CIVIC ENGAGEMENT AND GOVERNMENT SERVICES
- 26 14. TOURISM AND CULTURAL HERITAGE
- 27 CONCLUSION
In the 21st century, technology continues to advance at an unprecedented rate, fundamentally altering the way societies function and interact. One of the most transformative developments in recent years is the advent of 5G technology. As the fifth generation of wireless communication, 5G promises to deliver lightning-fast speeds, ultralow latency, and massive connectivity, all of which are crucial for the burgeoning fields of the Internet of Things (IoT) and smart city innovations. This article delves into the profound impact of 5G on IoT and smart cities, exploring how this technology is set to revolutionize urban living and drive a new era of interconnected, efficient, and sustainable environments.
UNDERSTANDING 5G TECHNOLOGY
Before examining the role of 5G in enabling IoT and smart city innovations, it is essential to understand what 5G technology entails. 5G, or fifth-generation wireless technology, is the latest iteration of mobile networks, following its predecessors 1G, 2G, 3G, and 4G. Each generation has brought significant improvements in speed, capacity, and connectivity, but 5G represents a quantum leap in performance and capabilities.
KEY FEATURES OF 5G:
- ENHANCED SPEED AND BANDWIDTH: 5G networks are designed to deliver data rates up to 10 Gbps, which is 100 times faster than 4G. This high-speed connectivity is essential for real-time applications and large-scale data transfers.
- ULTRA-LOW LATENCY: Latency, or the time it takes for data to travel from the sender to the receiver, is significantly reduced in 5G networks. With latency as low as 1 millisecond, 5G supports real-time communication and critical applications such as autonomous driving and remote surgery.
- MASSIVE DEVICE CONNECTIVITY: 5G can support up to one million devices per square kilometer, enabling the seamless integration of a vast number of IoT devices, sensors, and smart applications within a single network.
- NETWORK SLICING: 5G technology allows for the creation of multiple virtual networks within a single physical 5G network infrastructure. This capability enables customized services tailored to specific requirements, such as enhanced security for financial transactions or high reliability for industrial applications.
- ENERGY EFFICIENCY: 5G networks are designed to be more energy-efficient, extending the battery life of connected devices and reducing the overall energy consumption of the network.
THE INTERNET OF THINGS (IOT) AND ITS EVOLUTION
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the interconnected network of physical objects embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies to collect and exchange data. These objects, or “things,” range from everyday household items like refrigerators and thermostats to industrial machinery and transportation systems. The primary goal of IoT is to create a seamless and intelligent network that enhances efficiency, productivity, and decision-making across various sectors.
EVOLUTION OF IOT:
- EARLY BEGINNINGS: The concept of IoT dates back to the early 1980s when the first internet-connected devices were developed. However, it wasn’t until the advent of wireless technology and the proliferation of smartphones that IoT began to gain significant traction.
- PROLIFERATION OF CONNECTED DEVICES: The widespread adoption of smartphones and the development of wireless communication standards like Wi-Fi and Bluetooth paved the way for the rapid expansion of IoT devices. By the mid2010s, millions of devices were connected to the internet, generating vast amounts of data.
- ADVANCEMENTS IN SENSORS AND DATA ANALYTICS: The evolution of sensors and data analytics technologies has played a crucial role in the growth of IoT. Advanced sensors can now collect precise data on various parameters, while sophisticated data analytics tools enable real-time processing and analysis of this data.
- INTEGRATION WITH ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI): The integration of AI with IoT has further expanded its capabilities. AI algorithms can analyze data from IoT devices to identify patterns, predict outcomes, and automate decision-making processes.
THE SYNERGY BETWEEN 5G AND IOT
The synergy between 5G and IoT is poised to unlock unprecedented opportunities for innovation and transformation across various domains. The enhanced capabilities of 5G, such as high speed, low latency, and massive connectivity, are instrumental in addressing the limitations of current IoT deployments and enabling the next generation of IoT applications.
KEY BENEFITS OF 5G FOR IOT:
- REAL-TIME DATA PROCESSING: The ultra-low latency of 5G networks ensures that data from IoT devices can be processed in real-time. This capability is critical for applications that require immediate responses, such as autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and healthcare monitoring.
- SCALABILITY AND CONNECTIVITY: 5G’s ability to support a massive number of devices per square kilometer makes it ideal for large-scale IoT deployments. Cities, industries, and enterprises can connect and manage thousands or even millions of devices simultaneously without compromising performance.
- ENHANCED RELIABILITY AND SECURITY: 5G networks are designed to offer higher reliability and security compared to previous generations. Features like network slicing enable the creation of dedicated networks with customized security protocols, ensuring the safe and reliable operation of critical IoT applications.
- ENERGY EFFICIENCY: The energy-efficient design of 5G networks helps extend the battery life of IoT devices, reducing the need for frequent recharging and maintenance. This is particularly important for remote and hard-to-reach IoT installations.
- EDGE COMPUTING INTEGRATION: 5G’s architecture supports the integration of edge computing, where data processing occurs closer to the source of data generation. This reduces the latency and bandwidth requirements for IoT applications, enabling faster and more efficient data analysis.
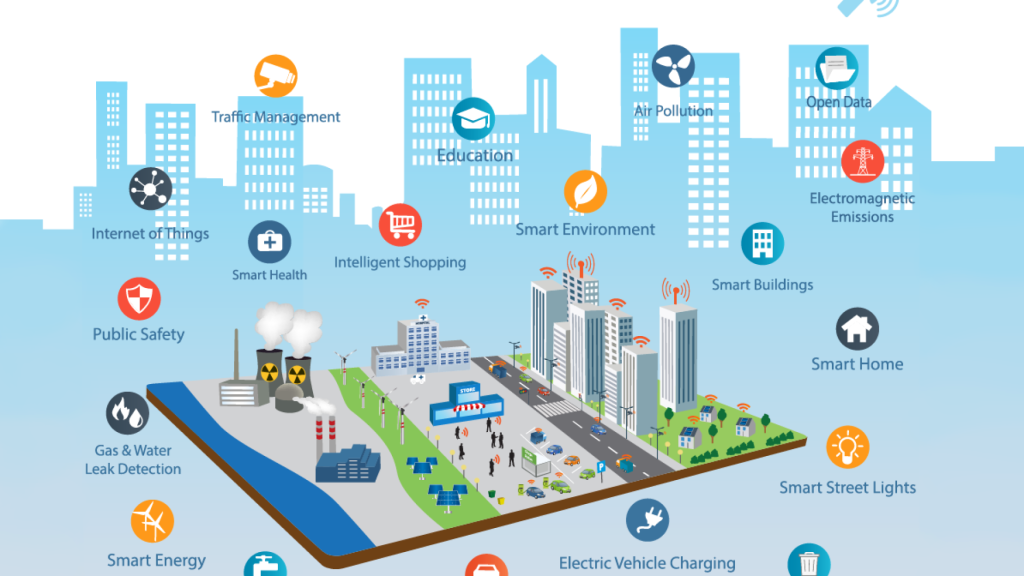
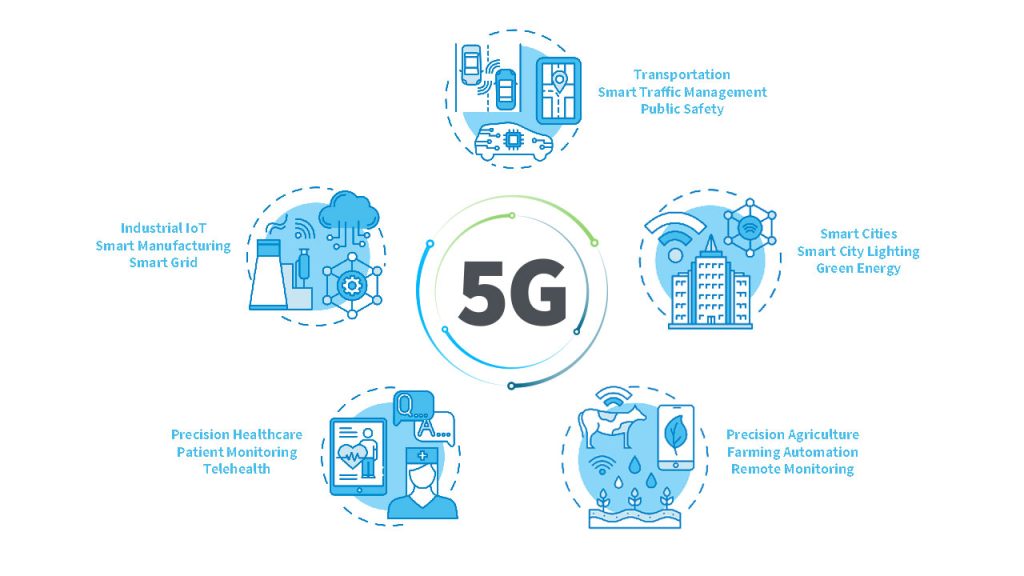
5G AND SMART CITY INNOVATIONS
Smart cities leverage advanced technologies, including IoT, AI, and big data analytics, to enhance the quality of life for their residents, improve operational efficiency, and promote sustainability. The deployment of 5G networks is a game-changer for smart city initiatives, providing the necessary infrastructure to support a wide range of innovative applications and services.
KEY AREAS OF IMPACT:
- SMART INFRASTRUCTURE AND UTILITIES:
Smart Grids: 5G enables the creation of smart grids that can monitor and manage energy consumption in real-time. Advanced sensors and meters can optimize energy distribution, reduce waste, and integrate renewable energy sources more effectively.
Water Management: IoT sensors connected via 5G can monitor water quality, detect leaks, and manage water distribution systems efficiently. This ensures a reliable and sustainable water supply for urban populations.
- INTELLIGENT TRANSPORTATION SYSTEMS:
Autonomous Vehicles: The low latency and high reliability of 5G networks are critical for the safe and efficient operation of autonomous vehicles. Real-time communication between vehicles, infrastructure, and pedestrians enhances traffic management and reduces accidents.
SMART TRAFFIC MANAGEMENT: IoT sensors and cameras connected through 5G can monitor traffic conditions in real-time, enabling dynamic traffic control and reducing congestion. Intelligent traffic lights can adjust their timing based on real-time traffic data, improving flow and reducing emissions.
- PUBLIC SAFETY AND SECURITY:
Surveillance and Monitoring: High-definition cameras and sensors connected via 5G can provide real-time surveillance and monitoring of public spaces. AI-powered analytics can detect anomalies, identify potential threats, and alert authorities promptly.
Emergency Response: 5G-enabled devices can enhance emergency response capabilities by providing real-time data and communication between first responders, medical personnel, and emergency services. This ensures faster and more coordinated responses to emergencies.
- HEALTHCARE AND WELLNESS:
Telemedicine: 5G facilitates high-quality video conferencing and real-time data sharing, making telemedicine more effective and accessible. Patients can consult with doctors remotely, reducing the need for physical visits and improving access to healthcare services.
REMOTE MONITORING: Wearable devices and sensors connected via 5G can continuously monitor patients’ health parameters and transmit data to healthcare providers in real-time. This enables proactive health management and timely interventions.
- ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING AND MANAGEMENT:
Air Quality Monitoring: IoT sensors connected through 5G can monitor air quality in realtime, providing valuable data for environmental management and policy-making. This helps cities take proactive measures to reduce pollution and protect public health.
Waste Management: Smart waste management systems can use IoT sensors to monitor waste levels in bins and optimize collection routes. This reduces operational costs and ensures efficient waste disposal.
- SMART BUILDINGS AND HOMES:
ENERGY MANAGEMENT: 5G-enabled smart buildings can optimize energy usage by monitoring and controlling lighting, heating, and cooling systems. This reduces energy consumption and lowers operational costs.
HOME AUTOMATION: 5G technology enhances the capabilities of smart home devices, enabling seamless control and automation of various household functions, from security systems to entertainment and appliances.
CHALLENGES AND CONSIDERATIONS
While 5G holds immense potential for enabling IoT and smart city innovations, several challenges and considerations need to be addressed to realize its full benefits.
- INFRASTRUCTURE INVESTMENT: Deploying 5G networks requires significant investment in infrastructure, including the installation of small cells, base stations, and fiber optic cables. Governments and private sector stakeholders must collaborate to fund and implement these networks effectively.
- DATA PRIVACY AND SECURITY: The proliferation of IoT devices and the vast amount of data generated pose significant privacy and security risks. Ensuring robust data protection measures and cybersecurity protocols is essential to safeguard sensitive information and maintain public trust.
- INTEROPERABILITY AND STANDARDS: The diverse range of IoT devices and platforms requires standardized protocols and interoperability to ensure seamless communication and integration. Industry stakeholders must work together to develop and adopt common standards.
- SPECTRUM ALLOCATION AND MANAGEMENT: 5G operates across a range of frequency bands, including low, mid, and high bands. Efficient spectrum allocation and management are crucial to prevent interference and ensure optimal performance. Regulatory bodies must develop policies that facilitate the equitable distribution of spectrum resources.
5. SKILL DEVELOPMENT AND WORKFORCE TRAINING:
The deployement and management of 5G networks and IoT systems require a skilled workforce. Investing in education and training programs is essential to equip professionals with the necessary skills to design, implement, and maintain these technologies.
6. ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT: While 5G technology can drive sustainability initiatives, the deployment of new infrastructure also has an environmental footprint. Careful planning and the adoption of eco-friendly practices are necessary to minimize the environmental impact of 5G rollouts.
CASE STUDIES OF 5G-ENABLED SMART CITIES
Several cities worldwide are already leveraging 5G technology to enhance their IoT ecosystems and drive smart city innovations. Here are a few notable examples:
1. SEOUL, SOUTH KOREA
Seoul is at the forefront of 5G deployment, with extensive network coverage and a wide range of smart city initiatives. The city uses 5G to support various applications, including:
SMART TRANSPORTATION: Seoul’s 5G-enabled transportation system includes real-time traffic monitoring, intelligent traffic lights, and connected public transportation. Autonomous buses and self-driving cars are being tested on city streets, enhancing mobility and reducing congestion.
PUBLIC SAFETY: High-definition cameras and IoT sensors connected via 5G monitor public spaces, providing real-time data to law enforcement agencies. AI-powered analytics help detect and respond to incidents quickly.
HEALTHCARE: Seoul’s healthcare system leverages 5G for remote patient monitoring and telemedicine services. Wearable devices track patients’ vital signs and transmit data to healthcare providers, enabling timely interventions and reducing hospital visits.
2. BARCELONA, SPAIN
Barcelona has been a pioneer in smart city initiatives, with a focus on sustainability and improving the quality of life for its residents. The city’s 5G deployment supports various projects, including:
SMART GRIDS: Barcelona uses 5G to enhance its energy management systems. Smart meters and sensors monitor energy consumption in real-time, optimizing distribution and integrating renewable energy sources.
ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING: IoT sensors connected via 5G monitor air quality, noise
levels, and water quality. This data helps the city implement policies to improve environmental conditions and public health.
SMART LIGHTING: Barcelona’s 5G-enabled street lighting system adjusts brightness based on real-time conditions, reducing energy consumption and enhancing public safety.
3. SINGAPORE
Singapore is known for its advanced infrastructure and technology-driven approach to urban development. The city-state’s 5G initiatives include:
AUTONOMOUS VEHICLES: Singapore is testing 5G-connected autonomous vehicles in designated areas. These vehicles communicate with each other and with infrastructure to navigate safely and efficiently.
SMART BUILDINGS: Singapore’s 5G-enabled smart buildings use sensors and IoT devices to optimize energy usage, enhance security, and improve occupant comfort. Building management systems monitor and control lighting, heating, cooling, and access.
PUBLIC SAFETY AND SECURITY: 5G-connected cameras and sensors enhance surveillance and emergency response capabilities. Real-time data from these devices helps authorities detect and respond to incidents promptly.
4. NEW YORK CITY, USA
New York City is leveraging 5G technology to enhance its urban infrastructure and services. Key initiatives include:
Smart Transportation: New York City’s 5G-enabled transportation system includes connected traffic signals, smart parking solutions, and real-time transit information. These innovations help reduce congestion and improve the efficiency of public transportation.
Public Wi-Fi: The city is deploying 5G-powered public Wi-Fi hotspots to provide high-speed internet access in underserved areas. This initiative aims to bridge the digital divide and ensure all residents have access to essential online services.
Healthcare and Telemedicine: New York City’s healthcare providers use 5G for telemedicine and remote patient monitoring. High-speed connectivity enables doctors to conduct virtual consultations and monitor patients’ health in real-time.
THE FUTURE OF 5G AND SMART CITIES
As 5G technology continues to evolve, its impact on IoT and smart city innovations will only grow stronger. The future promises even more advanced applications and services, driven by ongoing technological advancements and increased adoption.
1. INTEGRATION OF AI AND MACHINE LEARNING
The combination of 5G, AI, and machine learning will unlock new possibilities for smart cities. AI-powered analytics will process vast amounts of data generated by IoT devices, providing valuable insights for decision-making and automation. For example, predictive maintenance algorithms can identify and address infrastructure issues before they become critical, improving the efficiency and reliability of urban services.
2. ADVANCED ROBOTICS AND AUTOMATION
5G will enable the deployment of advanced robotics and automation systems in smart cities. From autonomous drones for delivery and surveillance to robotic assistants in healthcare and public services, these technologies will enhance productivity and service quality. The ultra-low latency and high reliability of 5G are essential for the real-time operation and coordination of these systems.
3. ENHANCED VIRTUAL AND AUGMENTED REALITY
The high-speed and low-latency capabilities of 5G will drive the adoption of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) applications in smart cities. These technologies can enhance various aspects of urban life, from immersive entertainment and virtual tourism to remote education and training. For example, AR can provide real-time navigation and information overlays, improving the experience of residents and visitors.
4. SUSTAINABLE URBAN DEVELOPMENT
5G will play a crucial role in promoting sustainability and resilience in smart cities.
Advanced IoT systems will monitor and manage energy usage, waste management, and environmental conditions more effectively. Smart grids and renewable energy integration will reduce carbon footprints, while efficient water and waste management systems will conserve resources and minimize pollution.
5. PERSONALIZED AND CITIZEN-CENTRIC SERVICES
The combination of 5G and IoT will enable the development of personalized and citizencentric services. Smart cities will leverage data from various sources to understand residents’ needs and preferences, delivering tailored services and experiences. For example, personalized public transportation options, customized healthcare plans, and targeted community engagement initiatives will enhance the overall quality of life.
6. ENHANCED PUBLIC TRANSPORTATION SYSTEMS
Public transportation systems in smart cities can greatly benefit from 5G connectivity. The ability to connect buses, trains, and other forms of public transit to a central network allows for real-time tracking, dynamic scheduling, and more efficient route management.
Here are some specific ways 5G can enhance public transportation:
DYNAMIC SCHEDULING: With real-time data on passenger numbers, traffic conditions, and vehicle locations, public transportation systems can adjust schedules dynamically to meet demand, reducing waiting times and improving service efficiency.
PREDICTIVE MAINTENANCE: Sensors on public transportation vehicles can monitor the condition of various components and predict when maintenance is needed, preventing breakdowns and reducing downtime.
ENHANCED PASSENGER EXPERIENCE: Passengers can benefit from real-time information about vehicle arrivals, seat availability, and route changes through mobile apps connected to the 5G network. In-vehicle entertainment and internet services can also be enhanced.
7. SMART HEALTHCARE SYSTEMS
The healthcare sector stands to gain significantly from the integration of 5G technology, especially in smart cities where advanced medical infrastructure and services are critical. Here are a few key applications:
REMOTE SURGERY: The ultra-low latency of 5G makes it possible for surgeons to perform
operations remotely using robotic systems. This can be particularly beneficial in emergency situations or in areas with limited access to specialized medical care.
CONTINUOUS PATIENT MONITORING: Wearable health devices connected via 5G can continuously monitor patients’ vital signs and transmit data to healthcare providers in realtime. This allows for better chronic disease management and early detection of potential health issues.
TELEMEDICINE: High-quality, real-time video consultations enabled by 5G can make telemedicine more effective, providing patients with access to healthcare services from the comfort of their homes.
8. SMART EDUCATION AND LEARNING ENVIRONMENTS
Education in smart cities can be significantly enhanced by 5G technology, offering new opportunities for interactive and immersive learning experiences. Key advancements include:
VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS: With the high-speed and low-latency capabilities of 5G, virtual classrooms can become more interactive and engaging, allowing for seamless collaboration between students and teachers regardless of their physical location.
AUGMENTED REALITY (AR) AND VIRTUAL REALITY (VR): 5G can support the use of AR and VR in education, providing immersive learning experiences that can make complex subjects more understandable and engaging. For instance, students can take virtual field trips or participate in interactive simulations.
PERSONALIZED LEARNING: Data from smart devices and learning platforms can be analyzed to provide personalized educational content and recommendations, helping students learn at their own pace and in a way that suits their individual needs.
9. ENHANCED RETAIL EXPERIENCES
The retail sector in smart cities can leverage 5G to enhance customer experiences and streamline operations. Here are some innovative applications:
SMART SHOPPING: Retail stores can use IoT sensors and 5G connectivity to offer smart shopping experiences. For example, smart shelves can automatically detect when products need restocking, and AR applications can provide customers with additional product information or personalized recommendations.
SEAMLESS PAYMENTS: 5G can facilitate fast and secure mobile payments, reducing checkout times and improving the overall shopping experience.
SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT: Retailers can use 5G-enabled IoT devices to track inventory and shipments in real-time, ensuring efficient supply chain operations and reducing the risk of stockouts or overstocking.
10. INTELLIGENT BUILDING MANAGEMENT
5G can transform the way buildings are managed in smart cities, making them more energy-efficient, secure, and comfortable for occupants. Key innovations include:
Energy Management: Smart buildings equipped with IoT sensors can monitor energy usage in real-time and optimize heating, cooling, and lighting systems to reduce energy consumption. This not only lowers operational costs but also contributes to sustainability goals.
Security Systems: 5G-enabled security cameras and access control systems can provide real-time monitoring and alerts, enhancing building security. AI-powered analytics can identify potential security threats and respond quickly.
Occupant Comfort: Smart buildings can adjust environmental conditions such as temperature, lighting, and air quality based on occupant preferences and real-time data, creating a more comfortable and productive living or working environment.
11. ENHANCED ENVIRONMENTAL SUSTAINABILITY
Smart cities with 5G networks can significantly enhance their environmental sustainability efforts. Here are some ways 5G can contribute to a greener future:
Smart Grids and Renewable Energy: 5G enables more efficient management of smart grids and integration of renewable energy sources. Real-time data from IoT devices helps balance supply and demand, reduce energy waste, and ensure a stable power supply.
Precision Agriculture: Urban agriculture and green spaces can benefit from 5G-enabled precision agriculture techniques. Sensors can monitor soil moisture, nutrient levels, and weather conditions, enabling efficient use of resources and higher crop yields.
Waste Management: Smart waste management systems use 5G-connected sensors to
monitor waste levels in bins and optimize collection routes. This reduces the environmental impact of waste collection and ensures timely disposal.
12. ADVANCED PUBLIC SAFETY AND EMERGENCY RESPONSE
5G technology can revolutionize public safety and emergency response in smart cities, making them more efficient and effective. Key applications include:
REAL-TIME SURVEILLANCE: 5G-enabled high-definition cameras and sensors can provide real-time surveillance of public spaces, enhancing situational awareness and enabling faster response to incidents.
CONNECTED EMERGENCY SERVICES: 5G connectivity allows for seamless communication and coordination between different emergency services, such as police, fire departments, and medical responders. Real-time data sharing ensures that responders have the information they need to act quickly and effectively.
DISASTER MANAGEMENT: In the event of natural disasters or other emergencies, 5G can support real-time monitoring and predictive analytics, helping authorities manage evacuations, allocate resources, and mitigate damage.
13. ENHANCED CIVIC ENGAGEMENT AND GOVERNMENT SERVICES
5G technology can improve the way governments interact with citizens and deliver services, fostering greater civic engagement and transparency. Here are some examples:
Digital Government Services: High-speed 5G networks enable the delivery of efficient and user-friendly digital government services, such as online permits, licenses, and public records. Citizens can access these services anytime and anywhere, reducing the need for in-person visits.
Participatory Platforms: 5G can support platforms that allow citizens to participate in decision-making processes, such as online forums, surveys, and voting systems. This promotes greater civic engagement and ensures that government policies reflect the needs and preferences of the community.
Smart City Dashboards: Real-time data from IoT devices and sensors can be integrated into smart city dashboards, providing citizens with up-to-date information on various aspects of city life, such as traffic conditions, air quality, and public services.
14. TOURISM AND CULTURAL HERITAGE
The tourism sector in smart cities can leverage 5G technology to create more immersive and personalized experiences for visitors. Key applications include:
AUGMENTED REALITY (AR) TOURS: Visitors can use AR applications on their smartphones or smart glasses to enhance their exploration of cultural and historical sites. AR can provide additional information, interactive content, and guided tours, making the experience more engaging and informative.
SMART HOSPITALITY: Hotels and other accommodations can use 5G-connected IoT devices to enhance guest experiences. For example, smart rooms can adjust lighting, temperature, and entertainment options based on guest preferences, and mobile checkin/check-out services can streamline the process.
REAL-TIME LANGUAGE TRANSLATION: 5G-enabled real-time language translation services can help tourists communicate more easily and navigate unfamiliar environments, enhancing their overall experience.
CONCLUSION
The advent of 5G technology marks a significant milestone in the evolution of wireless communication, offering unprecedented speed, reliability, and connectivity. As the backbone of IoT and smart city innovations, 5G is set to transform urban living, driving a new era of interconnected, efficient, and sustainable environments. From intelligent transportation systems and smart infrastructure to enhanced public safety and personalized services, the synergy between 5G and IoT holds immense potential for improving the quality of life for urban residents worldwide.
However, realizing the full potential of 5G and IoT in smart cities requires addressing several challenges, including infrastructure investment, data privacy and security, interoperability, spectrum management, workforce training, and environmental impact. By overcoming these challenges and fostering collaboration among stakeholders, we can pave the way for a future where technology enhances the well-being of society and creates more resilient and sustainable cities.
As cities continue to evolve and embrace the transformative power of 5G and IoT, the vision of smart, connected, and sustainable urban environments will become a reality, shaping the future of urban living for generations to come.